2. heapq
페이지 정보
작성자 관리자 댓글 0건 조회 6,143회 작성일 18-12-04 22:02본문
2. heapq
컬렉션 내부에서 가장 크거나 작은 N개의 아이템을 찾으려고 한다.
heapq 모듈에 이 용도에 적합한 nlargest()와 nsmallest() 함수가 있다.
- heapq.nlargest(n, iterable, key=None)
- heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable, key=None)
import heapq
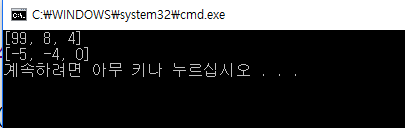
nums = [1, 8, 3, -5, 4, 99, -4, 0]
print(heapq.nlargest(3, nums))
print(heapq.nsmallest(3, nums))
좀 더 복잡한 구조에서는 키 파라미터에 람다를 전달해 가져올 수 있다.
import heapq
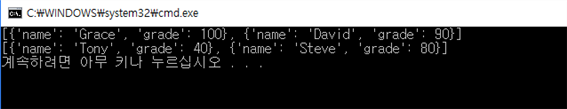
grades = [
{'name': 'Steve', 'grade': 80},
{'name': 'David', 'grade': 90},
{'name': 'Tony', 'grade': 40},
{'name': 'Grace', 'grade': 100}
]
print(heapq.nlargest(2, grades, lambda s: s['grade']))
print(heapq.nsmallest(2, grades, lambda s: s['grade']))
nlargest()와 nsmallest()는 N의 크기가 컬렉션의 크키보다 작은 경우에 유용하다. 실제로 위 함수는 아래처럼 데이터를 힙으로 정렬시켜 놓는 리스트로 변환한다.
import heapq
nums = [1, 8, 3, -5, 4, 99, -4, 0]
heap = list(nums)
heapq.heapify(heap)
print(heap)
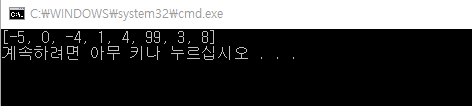
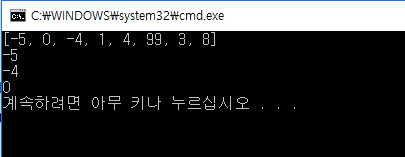
힙의 가장 중요한 기능을 heap[0]이 가장 작은 아이템이 된다는 사실이다. 가장 작은 아이템을 팝하고 그 다음 아이템으로 치환하는 heapq.heappop() 메서드를 사용하면, 뒤이어 나오는 아이템도 쉽게 찾을 수 있다.
print(heapq.heappop(heap))
print(heapq.heappop(heap))
print(heapq.heappop(heap))
만약 최대값이나 최소값을 찾는 경우라면(N = 1), min()이나 max()를 사용하는 것이 빠르다.
import heapq
nums = [1, 8, 3, -5, 4, 99, -4, 0]
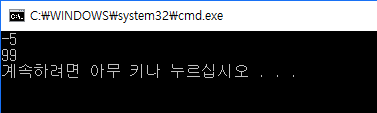
print(min(nums)) #-> -5
print(max(nums)) #-> 99
N의 크기가 컬렉션 크기와 비슷하다면, 컬렉션을 정렬해놓고 그 조각을 찾는 것이 더 빠르다.
import heapq
nums = [1, 8, 3, -5, 4, 99, -4, 0]
sorted_nums = sorted(nums)
print(sorted_nums[:3])
print(sorted_nums[-3:])
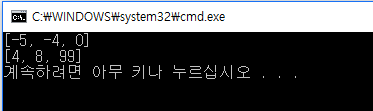
nlargest()의 결과와 정렬 순서가 다르다.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.
